U.S. elections are a cornerstone of American democracy, and at the heart of this process lies the state electoral votes map. This map plays a crucial role in determining the outcome of presidential elections, making it an essential topic for anyone interested in politics or civic engagement. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the state electoral votes map, exploring its significance, mechanics, and impact on the political landscape.
The state electoral votes map is more than just a visual representation of how each state contributes to the electoral college. It is a reflection of the nation's diversity, population distribution, and political dynamics. Understanding this map is vital for grasping how presidential elections are decided and why certain states carry more weight than others.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the state electoral votes map, breaking down complex concepts into digestible information. Whether you're a political enthusiast, a student, or simply someone curious about how elections work, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the intricacies of the electoral process.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to State Electoral Votes Map
- History of the Electoral College
- Mechanics of Electoral Votes
- Key Swing States in the Electoral Map
- Impact of Population on Electoral Votes
- Proposed Reforms to the Electoral System
- Challenges and Controversies
- Data and Statistics on Electoral Votes
- Future Trends in the Electoral Map
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to State Electoral Votes Map
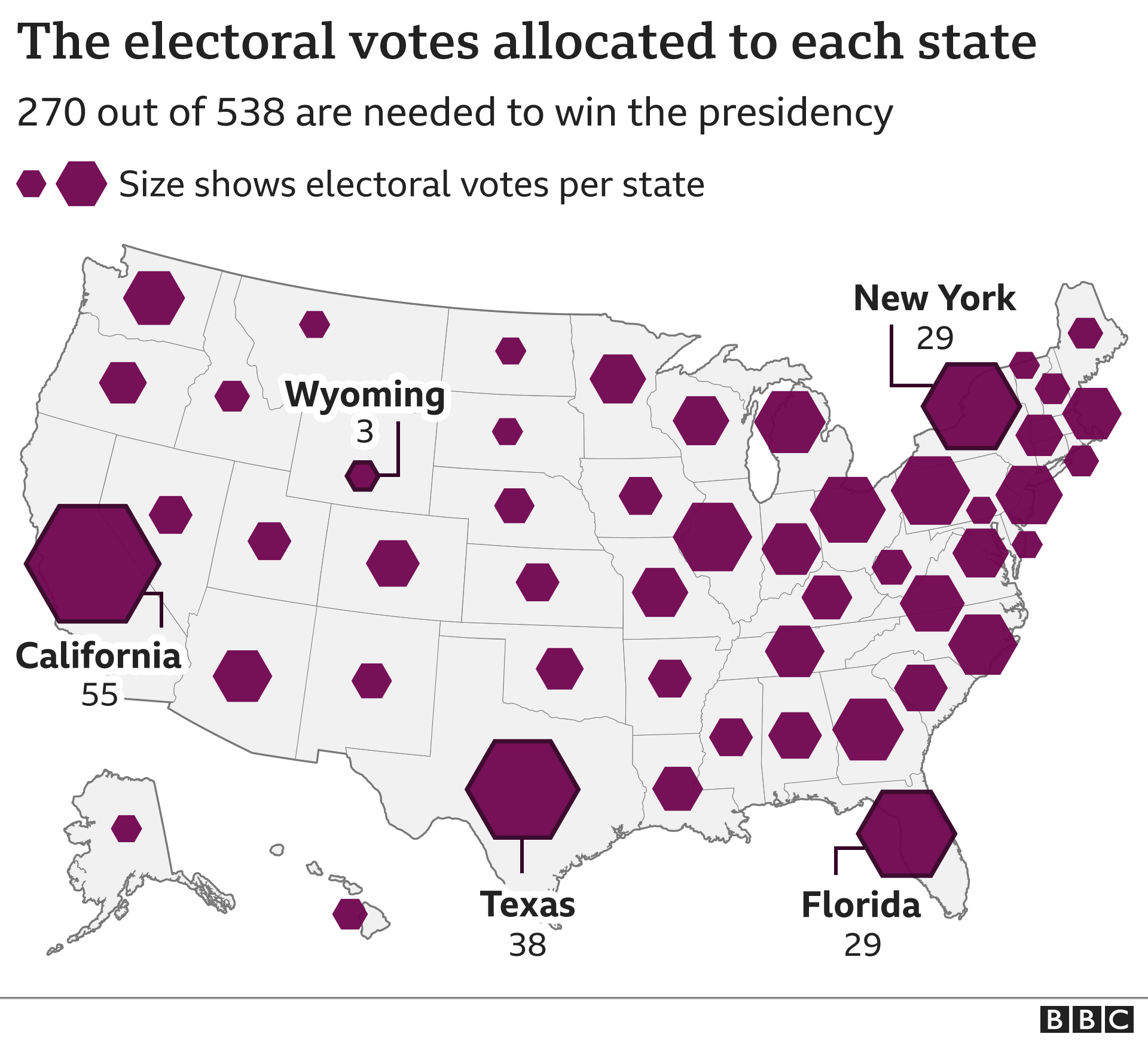
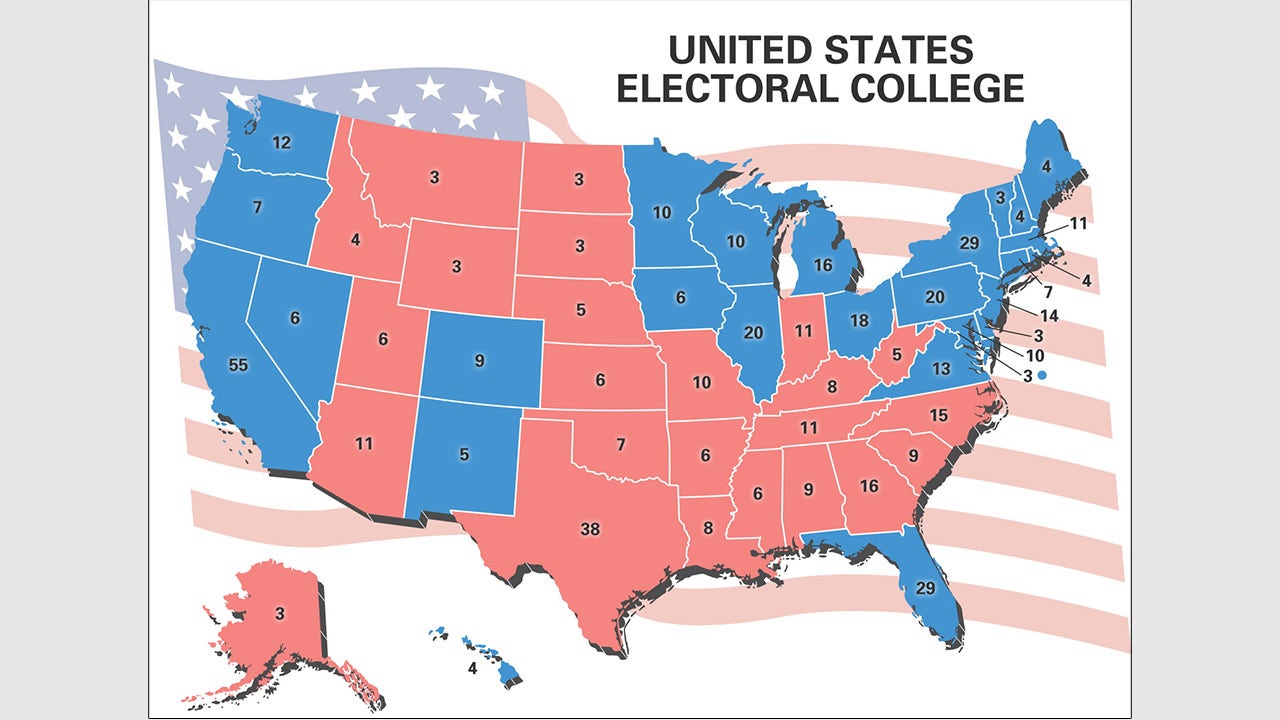
The state electoral votes map is a visual and numerical representation of how the United States allocates electoral votes to each state based on its population. Each state is assigned a specific number of electoral votes, which corresponds to the total number of its representatives in Congress (House of Representatives + Senate).
This map is updated every ten years following the national census, ensuring that the allocation of electoral votes reflects changes in population distribution. States with larger populations, such as California and Texas, have more electoral votes, while smaller states like Wyoming and Alaska have fewer.
Understanding the state electoral votes map is critical because it determines how presidential candidates strategize their campaigns. Swing states, or battleground states, often receive the most attention due to their potential to tip the balance in favor of one candidate or another.
History of the Electoral College
Origins of the Electoral System
The electoral college was established by the Founding Fathers as a compromise between direct popular vote and congressional selection of the president. It was designed to balance the interests of smaller and larger states, ensuring that no single group dominated the election process.
Evolution Over Time
Over the years, the electoral college has undergone several changes, primarily driven by population shifts and constitutional amendments. The 12th Amendment, ratified in 1804, clarified the process for electing the president and vice president, addressing ambiguities in the original system.
Despite these adjustments, debates about the electoral college's effectiveness and fairness continue to this day. Critics argue that it can lead to outcomes where the candidate with fewer popular votes wins the presidency, as seen in several historical elections.
Mechanics of Electoral Votes
How Electoral Votes Are Allocated
Each state's electoral votes are determined by adding the number of its representatives in the House of Representatives (based on population) to its two senators. For example, California, with 53 representatives and 2 senators, has 55 electoral votes, making it the most influential state in the electoral college.
Winning the Presidency
To win the presidency, a candidate must secure at least 270 electoral votes, which is a majority of the 538 total electoral votes. This requirement ensures that the winning candidate has broad-based support across the country, rather than relying solely on a few densely populated states.
In most states, the winner-takes-all system is employed, meaning the candidate who wins the majority of the popular vote in a state receives all of its electoral votes. However, Nebraska and Maine use a proportional system, allocating electoral votes based on the popular vote results in each congressional district.
Key Swing States in the Electoral Map
Definition of Swing States
Swing states, also known as battleground states, are those where the outcome of the election is uncertain and can swing either way. These states often have closely divided populations and play a decisive role in determining the winner of the presidential election.
Examples of Swing States
- Pennsylvania: Known for its diverse demographics and significant number of electoral votes.
- Florida: A key battleground state with a large population and 29 electoral votes.
- Wisconsin: Historically a swing state, with outcomes often reflecting national trends.
Candidates invest heavily in campaigning in these states, as securing their electoral votes can significantly boost their chances of winning the presidency.
Impact of Population on Electoral Votes
Population Distribution and Electoral Votes
Population distribution directly affects the allocation of electoral votes. States with growing populations, such as Texas and Florida, gain additional electoral votes after each census, while states with declining populations may lose votes.
Urban vs. Rural Influence
The urban-rural divide plays a significant role in shaping electoral outcomes. Urban areas tend to favor Democratic candidates, while rural areas lean toward Republicans. This dynamic influences how candidates tailor their messages and allocate resources during campaigns.
Proposed Reforms to the Electoral System
National Popular Vote Interstate Compact
One of the most discussed reforms is the National Popular Vote Interstate Compact, which aims to ensure that the candidate who wins the most popular votes nationwide becomes president. Under this system, participating states pledge to award all their electoral votes to the national popular vote winner.
Proportional Allocation
Another proposed reform is proportional allocation of electoral votes, similar to the systems used in Nebraska and Maine. This approach would allocate votes based on the percentage of the popular vote each candidate receives, potentially reducing the influence of swing states.
Challenges and Controversies
Disparities in Voting Power
One of the main criticisms of the electoral college is that it creates disparities in voting power between states. Smaller states have disproportionately more influence per capita than larger states, raising questions about fairness and representation.
Electoral College vs. Popular Vote
Instances where the electoral college winner does not align with the popular vote winner have sparked intense debates. Critics argue that this outcome undermines the principle of one person, one vote, while supporters contend that it preserves the balance between states.
Data and Statistics on Electoral Votes
Historical Trends
According to data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the Federal Election Commission, the distribution of electoral votes has shifted significantly over the past century. States in the South and West have gained prominence, reflecting broader demographic changes.
Key Statistics
- California holds the most electoral votes (55), followed by Texas (38).
- Smaller states like Wyoming and Alaska each have 3 electoral votes.
- Swing states like Florida and Pennsylvania consistently play pivotal roles in presidential elections.
Future Trends in the Electoral Map
Population Growth and Migration
Future trends in the electoral map will be shaped by population growth and migration patterns. States in the Sun Belt, including Arizona and Nevada, are expected to gain more electoral votes, while Rust Belt states may see a decline.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology and data analytics are transforming how campaigns approach the electoral map. Candidates now use sophisticated tools to target voters in specific states and districts, optimizing their chances of success.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, the state electoral votes map is a vital component of the U.S. electoral system, influencing how presidential elections are conducted and decided. By understanding its mechanics, history, and challenges, we can better appreciate the complexities of American democracy.
We encourage readers to engage with this topic further by exploring additional resources and participating in discussions about electoral reform. Your voice matters in shaping the future of our democratic processes. Share this article with others and consider exploring related topics on our website for a deeper understanding of U.S. politics.